Overview
Manufacturing and processing methods transform raw materials into functional products. They shape structure, control properties, and improve durability. For example, casting, welding, and coatings are used in many industries. In addition, emerging techniques like nanomanufacturing and micromanufacturing allow precision at the most minute scales.
Key Methods
- Casting – molten material shaped inside a mold.
- Powder Metallurgy and Sintering – powders compacted and heated to form dense solids.
- Plastic Deformation and Welding – mechanical methods for shaping and joining metals.
- Surface Treatments – coatings, thermal techniques, and chemical methods improve surface performance.
- Nanomanufacturing and Micromanufacturing – processes with precise control at small scales.
- Advanced Technologies – laser processing, electron beam treatment, and modern machining methods.
Each method offers specific advantages. For instance, casting is suited to significant components, while nanomanufacturing enables precision features. Therefore, engineers choose processes based on performance needs and application goals.
Surface Treatments and Coatings
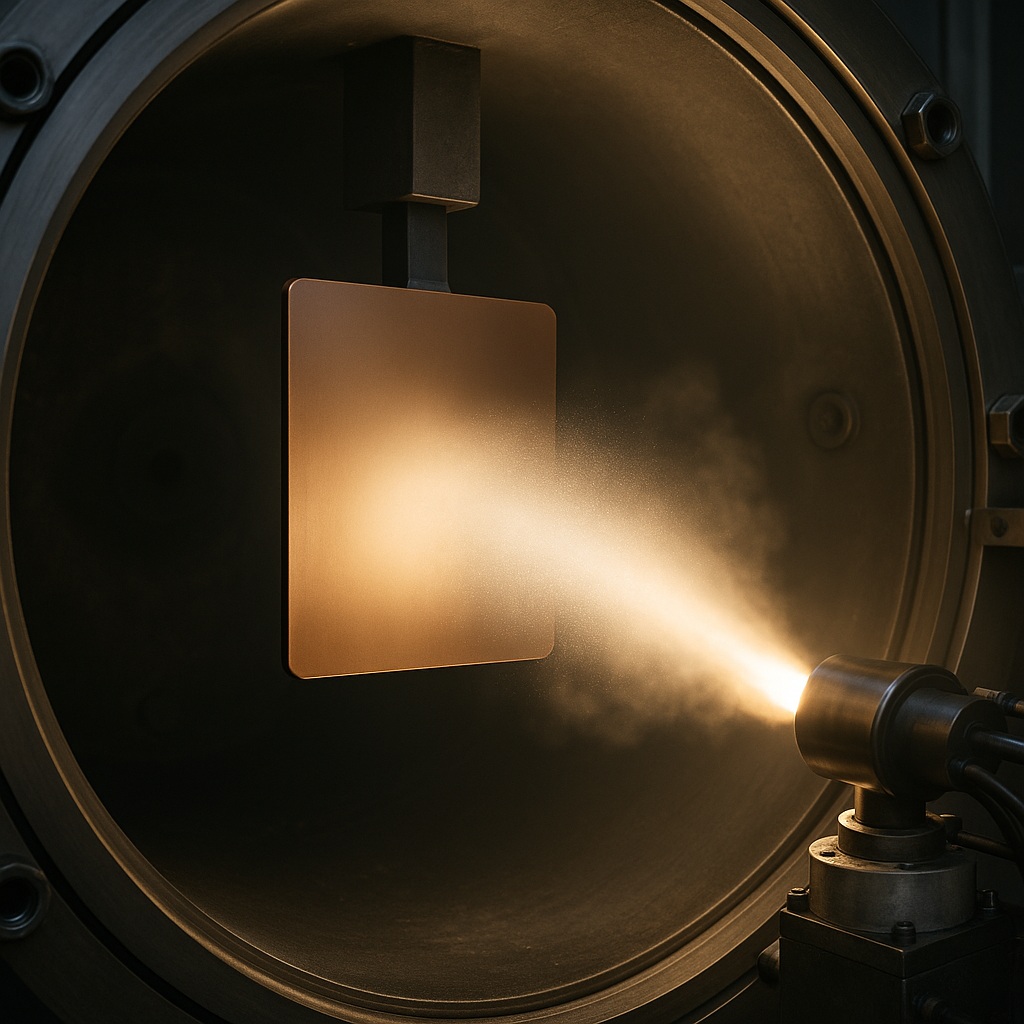
Surface engineering plays a central role in processing. Arc physical vapor deposition (PVD) creates hard, thin films on ceramic substrates. These films improve resistance to wear and extend service life. As a result, ceramics gain broader use in technical applications.
A study of arc PVD coatings applied fractal analysis to surface patterns. Researchers found that the coatings showed repeating structures across scales, known as fractal characteristics. This finding connects microstructure to material behavior, offering insight into durability and reliability.
Advanced Processing Technologies
Modern processing techniques expand possibilities beyond traditional methods. For instance, laser and electron beam treatments modify surfaces with high precision. Nanomanufacturing and micromanufacturing enable the design of features at extremely small dimensions. These approaches create coatings, films, and components with controlled properties. Moreover, advanced processing improves efficiency and reduces material waste.
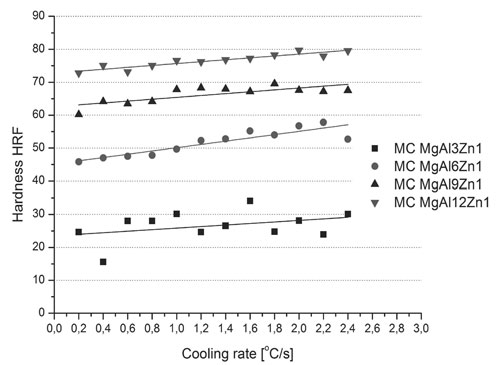
This figure demonstrates how processing conditions, such as cooling rate, affect material properties. It highlights the close relationship between manufacturing choices and final performance.
Conclusion
Manufacturing and processing methods define the function of engineering materials. Casting, welding, and sintering shape bulk structures. Coatings, nanomanufacturing, and laser treatments improve surface quality and extend performance. Overall, combining traditional processes with advanced methods provides efficient, durable, and adaptable solutions for materials science.